|
Extremes
Heat is energy. If you put more of it into the atmosphere and the
ocean, it will stir up more violent weather: heat-waves and droughts,
storms and floods.
The European heat-wave
of August 2003 was unlike anything ever seen before. The deaths
caused were about 35,000; in France alone, 18,000. In Britain, where
records had been kept since 1769, temperatures above 100° F (37.8°
C) were recorded for the first time — up to 101.3° F (38.5°)
in some places. There were nights when the heat never fell below
80° F. Records were also set in Portugal, Germany, and Switzerland.
The 2009 drought
in Kenya was the most prolonged and severe in memory. Coming on
top of the killing of elephants by poachers for ivory to smuggle
to China (many hundreds a year since the ban on ivory exports was
removed) drought conditions like this may, it is feared, drive elephants
to extinction in central and east Africa within 15 years.
In Somalia, the
rains used to fail about once in 10 to 12 years. This has begun
to happen almost every second year, sometimes two years in succession,
as in 2010 and 2011. The 2011 drought is one of the world's most
tragic. Thousands of thirsty people walked hundreds of miles —
many children becoming separated from their parents — to Kenya,
finding little or no relief when they got to overcrowded refugee
camps. How can a woman with four children aged from three to ten
walk for a month and a half across parched land?
Across the northern
half of China, huge sandstorms pin people indoors and can blow sand
as far as America. The number of these sandstorms has increased
six-fold (from about 4 to about 24 a year) in the past 50 years;
the factors causing this are overgrazing, deforestation, urban sprawl,
and increasingly erratic climate.
In England and Wales,
the floods of October 2000 were the worst on record. An Oxford University
study concluded in 2011 that the probable cause was global warming,
though the scientists cautiously did not express it quite that way:
what the massive processing of data showed was that modeling of
the probable weather gave up to a 90% greater chance of those floods
with than without the greenhouse gas we have put into the atmosphere.
Catastrophic flooding struck England again in 2010.
Layers of coral
in the Great Barrier Reef record fluctuations in the amount of fresh
water deriving from nearby rivers, hence give a chronology of wet
and dry years. Australian scientists found in 2011 that since the
end of the nineteenth century years of extreme rain or drought have
increased in frequency and intensity, results which “support
climate models suggesting that, as Earth warms, tropical rainfall
variability will increase.”
return.
Hurricane Sandy
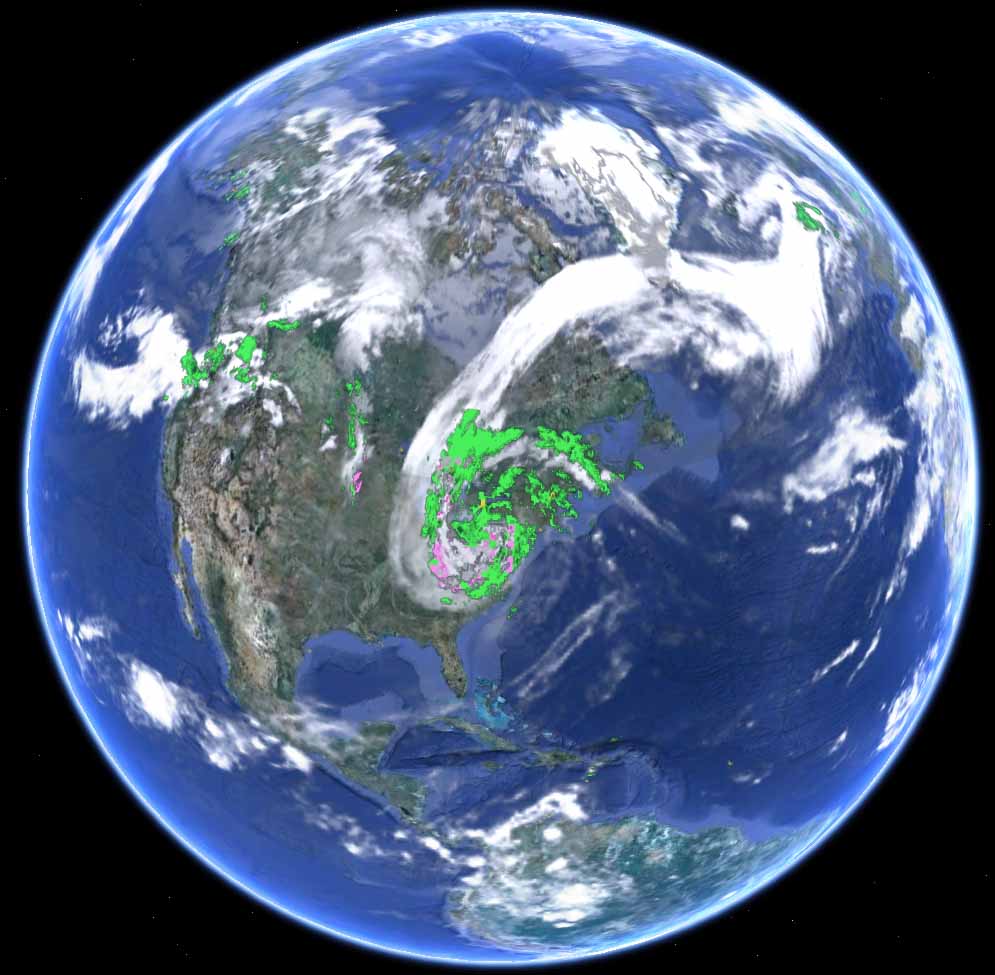
Hurricane Sandy, October 30, 2012
|


